Is it typical for individuals in their youth to experience receding gums? This article explores the common causes and risk factors at Young Age Receding Gums. By examining the signs and symptoms and the impact of poor oral hygiene, hormonal changes, lifestyle factors, genetic predisposition, and smoking habits on gum health, we can better understand this phenomenon. Additionally, strategies for prevention and treatment will be discussed to assist those in their 20s and 30s in maintaining optimal gum health.
Common Causes of Gum Recession in Young Adults
One common cause of gum recession in young adults is aggressive tooth brushing. When individuals brush their teeth too vigorously or use a toothbrush with stiff bristles, it can lead to the erosion of gum tissue and subsequent recession. Aggressive brushing can also damage the enamel of the teeth, causing further oral health issues. Additionally, wearing braces can have an impact on gum health. The pressure exerted by braces can cause gums to recede, especially if proper oral hygiene practices are not followed. Common treatments to address gum recession in young adults include scaling and root planing, which involves removing plaque and tartar from below the gum line and smoothing rough spots on the tooth roots. In severe cases, surgical procedures such as gum grafts may be necessary to restore lost tissue and prevent further recession. Young adults must maintain good oral hygiene and seek professional dental care to effectively prevent or treat gum recession.
Signs and Symptoms of Receding Gums in Early Adulthood
Typical indicators and manifestations of gum recession during the early adult years include exposed tooth roots, tooth sensitivity, and an elongated appearance of the teeth. Gum recession refers to the gradual loss of gum tissue around the teeth, leading to exposure of the underlying tooth structure. While it is more commonly associated with aging, young adults can also experience this condition for various reasons. Poor oral hygiene practices play a significant role in compromising gum health in young people. Inadequate brushing and flossing habits allow plaque and bacteria to accumulate along the gumline, leading to inflammation and eventual recession.
Aggressive brushing techniques or using a toothbrush with stiff bristles can also contribute to gum irritation and recession. Other factors contributing to gum recession in young adults include hormonal changes during puberty or pregnancy, genetic predisposition, smoking, certain medical conditions like diabetes or autoimmune diseases, misaligned teeth, or dental trauma. Young adults must adopt proper oral hygiene practices and seek professional dental care regularly to prevent or manage gum recession effectively.
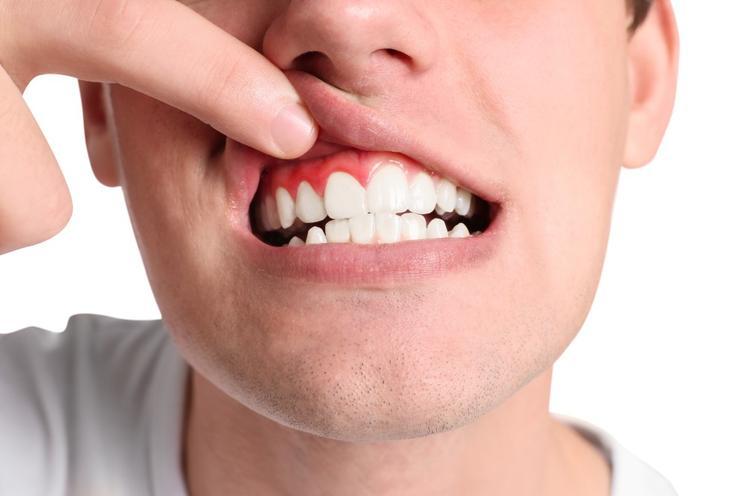

The Impact of Poor Oral Hygiene on Gum Health in Young People
Indicators and manifestations of poor oral hygiene in young individuals include the accumulation of plaque and bacteria along the gum line, leading to inflammation and eventual loss of gum tissue. Poor oral hygiene practices, such as inadequate brushing and flossing, can result in gingivitis, an early stage of gum disease characterized by swollen, red, and bleeding gums. If left untreated, gingivitis can progress to periodontitis, a more severe form of gum disease that can lead to tooth loss. Poor oral hygiene has also been linked to various systemic health conditions such as cardiovascular disease, diabetes, respiratory infections, and adverse pregnancy outcomes. Regular dental check-ups are crucial for maintaining good oral health as they allow for early detection and treatment of potential issues before they escalate. These check-ups also provide an opportunity for education on proper oral care techniques and reinforce the importance of maintaining good oral hygiene habits.
Hormonal Changes and Its Connection to Gum Recession
Hormonal changes during specific physiological processes can contribute to the development of gum recession. In pregnancy, hormonal changes play a significant role in altering oral health. Increased progesterone and estrogen levels during pregnancy can lead to an exaggerated response to plaque, causing inflammation and gum swelling, known as pregnancy gingivitis. This condition may eventually progress to gum recession if left untreated. Similarly, hormonal changes during puberty can also affect gum health. The surge in hormones, particularly sex hormones like estrogen and progesterone, can increase blood flow to the gums and make them more sensitive to irritants such as plaque and bacteria. Consequently, poor oral hygiene practices during this period may result in gum inflammation and potential recession. Therefore, it is crucial for individuals experiencing hormonal fluctuations during pregnancy or puberty to maintain proper oral hygiene practices and seek professional dental care to prevent or treat gum recession effectively.
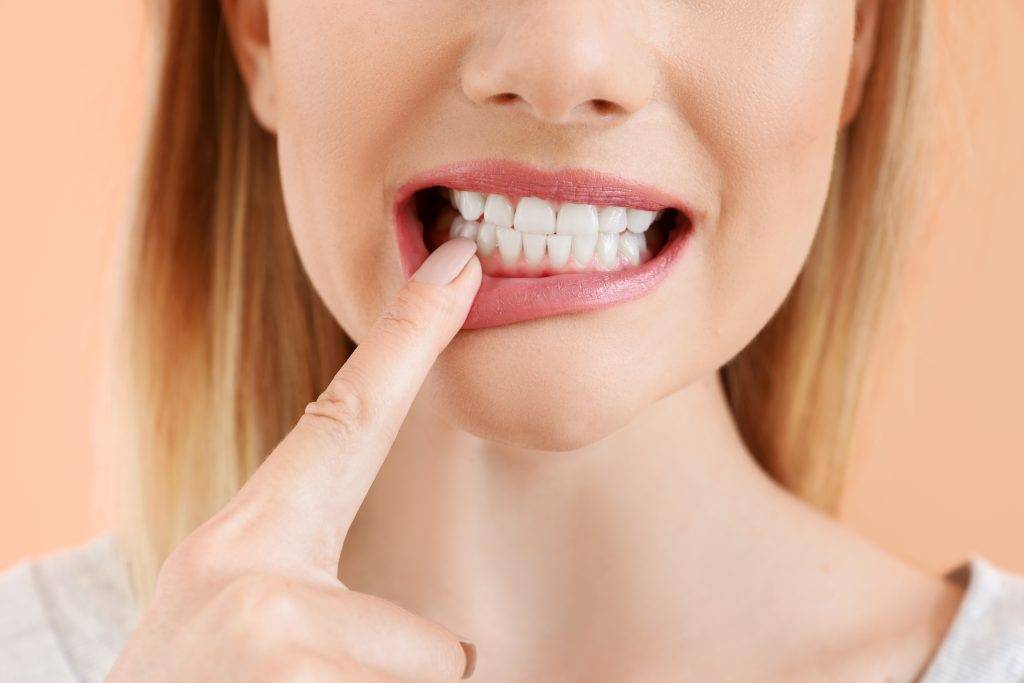

Lifestyle Factors That Contribute to Early Gum Recession
Various lifestyle factors, such as poor oral hygiene practices, smoking, and inadequate nutrition, have been identified as potential contributors to the early onset of gum recession. Maintaining good oral hygiene habits, including regular brushing and flossing, can help prevent plaque and bacteria buildup that can lead to gum disease and subsequent gum recession. Additionally, avoiding tobacco products and following a balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals can support gum health.
In addition to these factors, stress has also been suggested to play a role in gum health. Chronic stress may weaken the immune system and increase inflammation, potentially impacting the gums. However, further research is needed to understand the relationship between stress and gum recession.
To better understand the lifestyle factors associated with early gum recession prevention, consider the following table:
| Lifestyle Factors | Impact on Gum Health |
|---|---|
| Poor oral hygiene practices | Increases risk of plaque buildup |
| Smoking | Reduces blood flow to gums |
| Inadequate nutrition | Weakens immune system |
Genetic Predisposition to Gum Recession at a Young Age
Genetic factors have been identified as potential contributors to the early onset of gum recession. Hereditary gum recession is a condition that can occur in individuals who have inherited certain genetic traits related to their oral health. Research suggests that genetic factors significantly determine an individual’s susceptibility to gum recession at a young age. Some key points regarding the genetic predisposition to gum recession include:
- Variations in genes: Certain variations or mutations in specific genes involved in the immune response and tissue remodeling processes may increase the risk of developing gum recession.
- Family history: Individuals with a history of gum disease or periodontal problems are more likely to experience early onset gum recession due to shared genetic factors.
- Inflammatory response: Genetic variations can affect an individual’s inflammatory response, leading to an exaggerated immune reaction against bacteria and pathogens in the oral cavity, resulting in tissue damage and subsequent gum recession.
- Collagen production: Genetic factors can influence collagen production and structure, vital in maintaining healthy gums. Alterations in collagen metabolism may contribute to weakened gingival tissues and increased susceptibility to receding gums.
Understanding these genetic factors provides valuable insights into identifying individuals at risk for hereditary gum recession at a young age.
The Link Between Smoking and Receding Gums in Young Adults
Smoking has been identified as a potential risk factor for developing gum recession in young adults. Research suggests that smoking increases the likelihood of gum recession due to its adverse effects on oral health. Smoking cessation is crucial in preventing and reducing the progression of gum recession. Studies have shown that quitting smoking can positively impact overall oral health, including the prevention of gum disease and subsequent gum recession. Also, maintaining good dental care practices such as regular brushing, flossing, and professional cleanings can help prevent or slow down the progression of gum recession. To ensure proper treatment and management, seeking professional dental care and advice is recommended for young adults who smoke or have concerns about their gums.

Steps to Prevent and Treat Receding Gums in Your 20s and 30s
One practical approach to preventing and treating gum recession in individuals in their 20s and 30s is to adopt a comprehensive oral hygiene routine that includes regular brushing, flossing, and professional cleanings. This can help maintain good oral health and prevent the progression of gum recession. Other prevention techniques include avoiding tobacco use, as smoking has been linked to an increased risk of gum disease and recession. Also, maintaining a balanced diet low in sugary foods and drinks can help keep gums healthy. If gum recession does occur, several professional treatment options are available, such as scaling and root planing, gingival grafts, or dental implants. These treatments should be discussed with a dentist or periodontist to determine the most appropriate action for each individual’s case.

Damarion Haley stands as a prominent authority in the fields of Pediatric Dentistry and Dental Health Education, celebrated for her exceptional credentials and qualifications. Aims to provide a comprehensive insight into Damarion Haley’s impressive background, underscoring her pivotal role in the realm of children’s oral health and dental education.